suspension training workouts pdf
Suspension training is a versatile, portable workout method using suspension straps to engage the body against gravity. It enhances strength, flexibility, and balance, suitable for all fitness levels.
Essential Equipment for Suspension Training
The primary equipment for suspension training is a durable suspension strap system, such as the TRX Suspension Trainer. These straps are designed with adjustable lengths and sturdy anchors to support bodyweight exercises. Key components include:
- Straps: Made of high-quality, durable material to withstand regular use.
- Anchors: Can be mounted on walls, ceilings, or used as a portable option with a door anchor.
- Foot Cradles: Provide support and stability for exercises involving the legs.
- Handles: Adjustable and padded for comfort during workouts.
A sturdy anchor point is crucial for safety, ensuring the system can handle your weight. Optional accessories like grip covers or extension straps can enhance functionality. This minimal equipment setup allows for a full-body workout anywhere, making suspension training highly versatile and accessible. Proper equipment ensures safety and effectiveness in your training routine. Always inspect gear before use to avoid accidents.

Key Principles of Suspension Training
Suspension training revolves around leveraging your body weight as resistance while suspended in straps. The core principles include stability, control, and engaging the stabilizer muscles. The adjustable straps allow for varying difficulty by changing the angle of your body relative to the anchor point; Proper form is essential to prevent injury and maximize effectiveness. Breathing techniques and slow, controlled movements are emphasized to maintain balance and generate force. The system relies on functional movements that mimic real-life actions, promoting overall fitness and mobility. Mastery of these principles ensures a safe and effective workout, targeting strength, flexibility, and coordination simultaneously. Consistency and progressive overload are key to achieving long-term results in suspension training. Always focus on proper technique to reap the full benefits of this versatile training method.
Benefits of Suspension Training
Suspension training offers numerous benefits, including improved strength, flexibility, and balance. It engages the entire body, promoting functional fitness and core stability. The portable nature of suspension equipment makes it ideal for workouts at home, outdoors, or in a gym. By leveraging body weight as resistance, it allows for scalable intensity, catering to all fitness levels. Suspension training also enhances proprioception and coordination, reducing injury risk. Additionally, it boosts metabolism and burns calories effectively. The low-impact nature of suspension exercises makes it suitable for those with joint issues or recovering from injuries. Overall, suspension training provides a versatile, efficient, and engaging way to achieve a full-body workout, making it a popular choice for fitness enthusiasts worldwide. Its adaptability ensures continuous progress, keeping workouts fresh and challenging.
Getting Started with Suspension Training
Getting started with suspension training is straightforward and accessible for all fitness levels. Begin by familiarizing yourself with the equipment, such as suspension straps or a TRX trainer. Ensure the equipment is securely anchored to a sturdy object, and adjust the straps to the appropriate length for your exercises. Start with basic movements like planks, rows, and chest presses to build confidence and proper form. Focus on engaging your core and maintaining control throughout each movement. Gradually increase the difficulty by changing your body position or adding more dynamic movements. Warm up before each session and cool down afterward to prevent injury. Consistency is key to seeing results, so aim to incorporate suspension training into your routine 2-3 times per week. Track your progress and adjust your workouts to keep challenging yourself.

Upper Body Exercises
Upper body exercises in suspension training target chest, shoulders, and triceps. Key exercises include TRX Chest Fly, Atomic Push-Up, and Back Rows, enhancing strength and stability effectively.
6.1 Push Exercises
Push exercises in suspension training are designed to engage the chest, shoulders, and triceps. A fundamental movement is the TRX Push-Up, where the feet are suspended, challenging core stability. The Chest Press involves holding the straps and pressing forward, targeting the chest muscles. Flys are performed by spreading the arms wide, emphasizing shoulder and chest engagement. These exercises can be modified by adjusting body angle or adding plyometric movements. Proper form ensures effectiveness and prevents injury. Incorporating variations like single-arm presses or decline push-ups caters to different fitness levels. Push exercises enhance upper body strength, improve posture, and build muscle endurance. They are versatile for both beginners and advanced trainees, offering scalable intensity. Consistency in these exercises yields noticeable improvements in overall upper body development and functional fitness.
6.2 Pull Exercises
Pull exercises in suspension training focus on strengthening the back, shoulders, and arms. The TRX Row is a cornerstone, where you pull your body toward the anchor, engaging the latissimus dorsi and rhomboids. The Bicep Curl targets the biceps by bending the elbows and pulling the straps toward the body. Other variations include Single-Arm Rows and Lateral Pulls, which add diversity and challenge. These exercises improve posture, enhance upper body strength, and promote muscle balance; Adjusting body angles or resistance levels allows for progression. Proper form is crucial to avoid injury, emphasizing controlled movements and core engagement. Pull exercises complement push exercises, creating a well-rounded workout. They are adaptable to all fitness levels, making them a valuable addition to any suspension training routine. Consistent practice leads to noticeable gains in strength and overall physique.
Lower Body Exercises
Suspension training effectively targets the legs, glutes, and core with exercises like squats, lunges, and single-leg movements. These exercises improve strength, stability, and functional mobility while enhancing overall lower body endurance. Variable resistance and controlled movements promote balanced development and injury prevention. Proper form and progression are key to maximizing results and maintaining safety. Suspension training for the lower body is versatile, suitable for all fitness levels, and ideal for building a strong foundation; Regular practice enhances athletic performance and daily functionality.
7.1 Squats
Suspension training squats are a dynamic exercise that strengthens the legs, glutes, and core while improving balance and mobility. Using the suspension straps for resistance, you can perform bodyweight squats with increased intensity. The movement involves lowering the body with control, keeping the chest upright and knees aligned with toes. Suspension squats engage the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes effectively, while the instability of the straps challenges the core for stability. This exercise promotes functional strength and can be modified to suit different fitness levels. For added challenge, single-leg squats can be incorporated to target imbalances and enhance unilateral strength. Proper form is crucial to avoid injury, ensuring the back remains neutral and the movement is smooth. Regular practice improves overall lower body strength, power, and coordination, making suspension squats a versatile and effective addition to any workout routine.
7.2 Lunges
Suspension lunges are a powerful exercise for building strength, balance, and coordination in the lower body. By incorporating suspension straps, this variation adds instability, which engages the core and challenges balance. Suspension lunges target the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and hip flexors, while also improving functional movement patterns. The exercise involves stepping forward or backward while maintaining tension in the straps, ensuring proper form to avoid injury. The added resistance from the straps intensifies the workout compared to traditional lunges. Modifications, such as changing the depth or angle, allow for customization to fitness levels. Single-leg lunges can further enhance balance and strength. This exercise is excellent for developing unilateral strength and addressing muscle imbalances. Regular practice improves overall lower body stability and functional fitness, making suspension lunges a valuable addition to any suspension training routine.
Core Exercises
Suspension training enhances core stability by engaging the abdominals and lower back muscles. It improves balance, posture, and overall functional strength through dynamic movements and controlled instability.
8.1 Planks
Planks are a cornerstone of suspension training, targeting the core, shoulders, and back muscles. Using suspension straps, plank variations like forearm planks or straight-arm planks can be performed. The instability of the straps increases muscle engagement, particularly in the abdominals and obliques, improving overall core stability. To perform, position your feet in the straps and maintain a straight line from head to heels, engaging your core and holding the position for 30-60 seconds. This exercise enhances posture, reduces lower back pain, and boosts functional strength. Proper form is crucial; keep your body rigid and avoid letting your hips sag. For advanced users, planks can be modified by adding leg lifts or lateral shifts. Regular practice improves endurance and strengthens the entire core, essential for stability in other suspension exercises.
8.2 Rotational Movements
Rotational movements in suspension training target the obliques and rotational strength, essential for functional stability and power. Exercises like the rotational press or rotational pull engage the core while improving coordination and balance. To perform, stand facing the anchor point with the straps at hip height. Grip the handles and press or pull while rotating your torso, maintaining control throughout the motion. These movements mimic real-life actions, such as swinging a golf club or throwing a punch, enhancing athletic performance. Keep your core engaged and focus on smooth, controlled rotations to maximize effectiveness. Rotational movements also improve posture and reduce the risk of injury by strengthening the muscles around the spine. Incorporate variations like single-arm or alternating rotations to challenge different muscle groups and enhance overall core stability. Proper form ensures safety and optimal results.

Programming Your Workouts
Programming your suspension training workouts involves creating structured routines that align with your fitness goals, focusing on exercise selection, frequency, duration, and intensity to ensure progress and consistency.
9.1 Structuring Effective Routines
Structuring effective suspension training routines requires a balanced approach to ensure overall fitness and progression. Begin by defining clear fitness goals, whether strength, endurance, or weight loss. Design workouts that target all major muscle groups, alternating between upper body, lower body, and core exercises. Incorporate variations of exercises to maintain engagement and prevent plateaus. Start with foundational movements like push presses, rows, and squats, gradually increasing intensity by adjusting angles or resistance. Include dynamic warm-ups and finish with stretching to enhance mobility. Aim for 3-4 sessions per week, allowing rest days for recovery. Tailor routines to individual fitness levels, adjusting volume and intensity accordingly. Consistency and progression are key to achieving long-term results. Always prioritize proper form to minimize injury risks and maximize effectiveness.
9.2 Sample Workout Plan
A sample suspension training workout plan might look like this:
– Day 1 (Upper Body Focus):
⎻ Suspension push-ups (3 sets of 12 reps)
⎻ Chest presses (3 sets of 10 reps)
⏤ Lateral slides (3 sets of 15 reps)
⎻ Tricep dips (3 sets of 12 reps)
– Day 2 (Lower Body Focus):
⎻ Suspension squats (3 sets of 12 reps)
⏤ Lunges (3 sets of 10 reps per leg)
⏤ Calf raises (3 sets of 15 reps)
– Day 3 (Core Focus):
⏤ Plank rows (3 sets of 12 reps)
⏤ Knee tucks (3 sets of 15 reps)
⎻ Side planks (3 sets of 20 seconds hold per side)
– Day 4 (Active Recovery):
⎻ Gentle suspension stretches (10-15 minutes)
– Day 5 (Full Body Focus):
⎻ Burpees (3 sets of 10 reps)
⎻ Mountain climbers (3 sets of 30 seconds)
⏤ Suspension rows (3 sets of 12 reps)
– Day 6 (Core & Mobility):
⏤ Russian twists (3 sets of 12 reps)
⎻ Leg swings (3 sets of 15 reps per leg)
– Day 7 (Rest Day):
⏤ Light cardio or yoga (optional)
Adjust reps, sets, and intensity based on fitness level and goals. Warm up before each session and cool down afterward.
Safety Tips and Precautions
Ensuring safety is crucial when performing suspension training workouts. Always inspect the equipment before use to check for wear and tear. Proper form and technique are essential to avoid injuries, so start with lighter exercises and gradually increase intensity. Warm up thoroughly before each session and cool down afterward to prevent muscle strain. Use a spotter when attempting advanced movements. Listen to your body and rest when needed to avoid overexertion. Stay hydrated throughout your workout. Avoid training on an empty stomach or when overly fatigued. Ensure the suspension system is securely anchored to a stable structure. If you have pre-existing injuries, consult a professional before starting. Always have a first aid kit nearby. By following these guidelines, you can minimize risks and enjoy a safe, effective suspension training experience.
Psychological Aspects of Training
Mental preparedness plays a vital role in suspension training. Developing a strong mindset helps overcome challenges and maintain consistency. Focus on setting achievable goals to stay motivated and track progress. Building mental resilience is key to pushing through difficult workouts. Positive self-talk and visualization can enhance performance and confidence. Training with a partner or group can foster accountability and camaraderie. Celebrating small victories boosts morale and reinforces commitment. Understanding your “why” keeps you driven during tough moments. Embrace the process, and remember that mental strength is as important as physical strength in suspension training. By cultivating a positive and resilient mindset, you can unlock your full potential and enjoy a rewarding fitness journey.
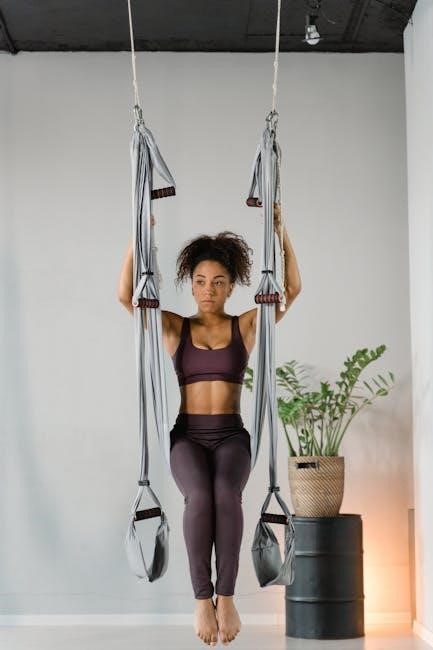

Advanced Techniques
Once mastery of basic exercises is achieved, advanced techniques can elevate your suspension training. Progressions involve increasing difficulty by altering angles or reducing stability. Regressions modify movements to suit intermediate levels. Movement variations, such as tempo changes or pause reps, enhance intensity. Multi-planar exercises, like rotational movements, challenge stability and strength. Unilateral training targets specific muscle groups. Dynamic movements, such as explosive pulls or rapid transitions, improve power and coordination. Incorporating plyometric elements adds intensity. Proper form and control are crucial to prevent injury. Exploring these techniques keeps workouts engaging and ensures continuous progress. Examples include single-arm or single-leg exercises, or “around-the-worlds” for multi-directional challenge. Consistency and patience are key to mastering advanced techniques and maximizing results.
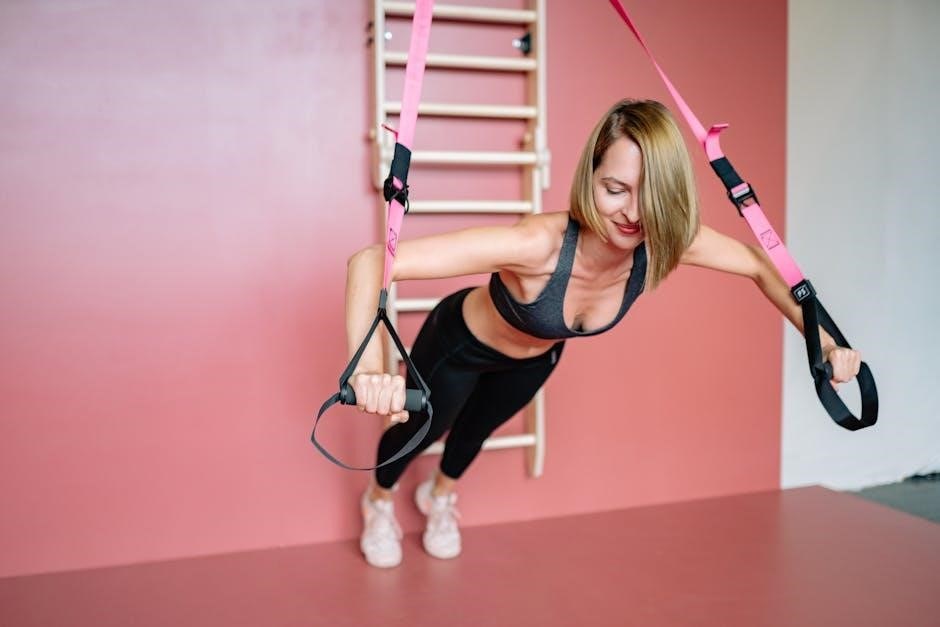

Warm-Up Routines
A proper warm-up is essential before starting any suspension training workout. It prepares the body for physical activity, reduces the risk of injury, and enhances performance. Begin with 5-10 minutes of light cardio, such as jumping jacks or jogging in place, to increase blood flow and heart rate. Dynamic stretching, like arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists, helps improve flexibility and mobility. Incorporate suspension-based movements, such as gentle rows or squats, to activate the muscles. Focus on controlled, slow movements to engage the core and stabilize the body. Gradually increase intensity to prepare for more demanding exercises. A well-structured warm-up ensures a safe and effective workout. Always prioritize proper form and breathing to maximize results and prevent strain.
Cool Down and Stretching
A proper cool-down after suspension training is crucial for recovery and muscle relaxation. Begin with 5-10 minutes of static stretching to target major muscle groups, such as hamstrings, quadriceps, and chest muscles. Use suspension straps to assist in deep, controlled stretches, like a standing hamstring stretch or seated forward bend. Incorporate deep breathing exercises to reduce heart rate and promote relaxation. Focus on holding each stretch for 20-30 seconds to maximize flexibility. Gentle movements, such as arm circles or leg swings, can help gradually lower intensity. Foam rolling or self-myofascial release can also aid in muscle recovery. End with a minute of seated or standing meditation to transition smoothly from exercise to rest. A well-executed cool-down enhances recovery, reduces soreness, and prepares the body for future workouts.
Nutrition for Optimal Performance
Nutrition plays a vital role in maximizing the benefits of suspension training. A balanced diet rich in protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats is essential to fuel workouts and support muscle recovery. Prioritize lean protein sources like chicken, fish, and eggs to repair and build muscle tissue. Complex carbs, such as whole grains and vegetables, provide sustained energy for intense sessions. Hydration is critical, so drink plenty of water before, during, and after training. Aim to eat a balanced meal 1-3 hours before workouts and refuel with a protein-rich snack or meal within 30-60 minutes post-exercise. Avoid processed foods and focus on whole, nutrient-dense options to optimize performance and recovery. Consistency in nutrition will enhance endurance, strength, and overall results in suspension training.
Tracking Progress and Improvement
Monitoring progress is essential to ensure continuous improvement in suspension training. Start by setting clear, measurable goals and tracking workouts consistently. Use a log to record exercises, sets, reps, and resistance levels. Over time, observe increases in strength, endurance, and mobility. Take progress photos or measurements to visually assess changes. Incorporate benchmark exercises, such as chest presses or rows, to measure strength improvements. Track workout frequency and volume to ensure consistency. Celebrate small victories to stay motivated, and adjust routines as needed. Regularly reassess goals to align with new fitness levels. A progress tracking chart or app can help visualize advancements. By systematically monitoring improvements, you can optimize your suspension training journey and achieve long-term success.
Suspension training is a versatile and effective method for building strength, improving flexibility, and enhancing overall fitness. Its portability and scalability make it accessible to individuals of all fitness levels. By incorporating suspension training into your routine, you can achieve a full-body workout that challenges stability, engages the core, and promotes functional movement. Consistent practice and proper form are key to maximizing results. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced athlete, suspension training offers endless opportunities for growth. With dedication and the right approach, you can unlock its full potential and achieve your fitness goals. Start your suspension training journey today and experience the transformative benefits it has to offer. Remember to stay consistent, challenge yourself, and celebrate your progress along the way.
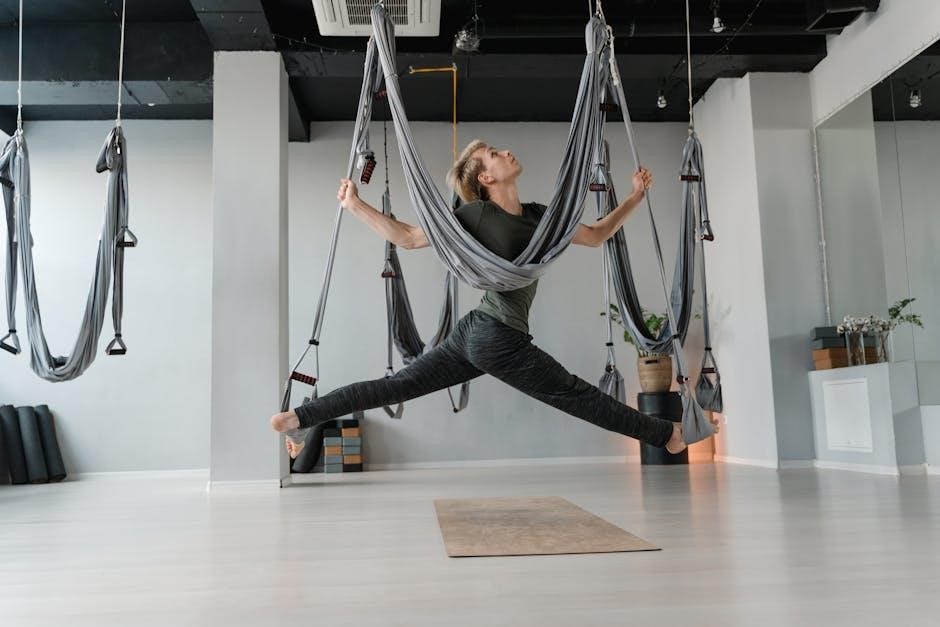

Additional Resources
For further exploration and enhancement of your suspension training journey, consider the following resources:
- Official TRX Website: A comprehensive source for suspension training equipment, workout plans, and instructional videos.
- YouTube Channels: Channels like TRX Training and other fitness influencers offer diverse workout routines and tutorials to complement your PDF guide.
- Mobile Apps: Apps such as TRX Training provide customizable workout plans, timers, and progress tracking features to optimize your training.
- Books and eBooks: Titles like “TRX Suspension Training” offer detailed guides and workout plans for all fitness levels.
- Online Forums: Communities like Reddit’s r/Fitness or specialized Facebook groups share tips, challenges, and resources.
- Certification Programs: Advanced training courses for those interested in mastering suspension training techniques or teaching others.
These resources will help you deepen your understanding and diversify your workouts, ensuring continuous progress and engagement.

Final Thoughts and Encouragement
Congratulations on completing this comprehensive guide to suspension training! By now, you’ve gained valuable insights into how to harness the power of suspension training to transform your fitness journey. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced athlete, suspension training offers a versatile and effective way to build strength, improve flexibility, and enhance overall fitness.
Remember, consistency is key. Start with the basics, gradually increase intensity, and celebrate small victories along the way. Stay committed, and you’ll soon experience the transformative power of suspension training firsthand. Don’t hesitate to explore additional resources or seek guidance to refine your skills. Most importantly, embrace the process, stay motivated, and enjoy the journey toward a stronger, healthier you!
